General Medicine Internship Real Patient OSCEs towards optimizing clinical complexity
Introduction: This online E-log Entry Blog is an objectively structured clinical examination method to assess the clinical competence during the course of my General Medicine Internship rotation (June'2023-August'2023) by reviewing the case reports shared below and to discuss, understand and review the clinical scenarios and data analysis of patients so as to develop my clinical competency in comprehending clinical cases, and providing evidence-based inputs for questions surrounding the clinical vignettes borrowed from the E Log Book.
Note: The cases have been shared after taking consent from the patient/guardian. All names and other identifiers have been removed to secure and respect the privacy of the patient and the family.
Amc case no:1
Patient came to with the complaints of abdominal distension since 20 days
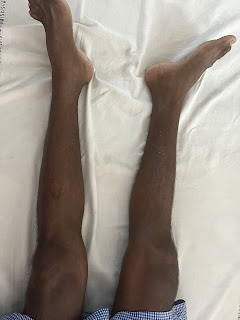
Pedal edema since 1 week
Detailed history: Patient was a home maker developed abdominal distension since 20 days and pedal edema since 1 week
Pt was apparently asymptomatic 20 days ago then she developed abdominal distension, which was insidious in onset, gradually progressive in nature
The test also measures the ratios of two liver enzymes, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT).
Acute hepatitis C is a short-term viral infection. People with acute hepatitis C carry the infection for a small window of time, often just several months
Acute hepatitis C may improve or resolve without treatment. It leads to chronic infection in 75 to 85% of cases. The chronic form may cause long-term problems in your liver, including liver damage and liver cancer.
Transmission:
HCV is spread through direct contact with blood or certain bodily fluids that contain HCV.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of acute hepatitis C range from very mild to severe. They include:
- nausea
- vomiting
- loss of appetite
- fever
- fatigue
- abdominal pain
- joint pain
- dark urine
- light, clay-colored bowel movements
- jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes
7)Ribavirin uses and side effects?
Ans:Ribavirin oral tablet is used in combination with other drugs to treat chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. It’s used for people with HCV alone, and those with both HCV and HIV.
https://www.healthline.com/health/drugs/ribavirin-oral-tablet
8)what is portal hypertension it’s causes and treatment?
Ans:The portal vein carries blood from stomach, pancreas, and other digestive organs to liver. It differs from other veins, which all carry blood to your heart.
The liver plays an important role in circulation. It filters out toxins and other waste matter that the digestive organs have deposited in bloodstream. When the blood pressure in the portal vein is too high, then portal hypertension occurs.
https://www.healthline.com/health/portal-hypertension
9)what is child-Pugh score?
Ans:The Child-Pugh score is a system for assessing the prognosis — including the required strength of treatment and necessity of liver transplant — of chronic liver disease, primarily cirrhosis.It provides a forecast of the increasing severity of your liver disease and your expected survival rate.
https://www.healthline.com/health/child-pugh-classification
10)Decompensated liver disease symptoms and treatment?
Ans:Decompensated liver disease is also known as decompensated cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease that’s commonly the result of hepatitis or alcohol use disorder. Cirrhosis is the severe scarring of the liver seen at the terminal stages of chronic liver disease. When your liver is damaged, scar tissue is formed as it tries to repair itself.
https://www.healthline.com/health/decompensated-liver-disease
11)What are the differences between acute and chronic hepatitis c ?
Ans:
- Acute hepatitis C is the
early stage when you’ve had hepatitis for less than six months. - Chronic hepatitis C isthe long-term type, which means you’ve had the condition for at least six months.
- Up to 85 percen
t hepatitis C will eventually develop the chronic form of the disease